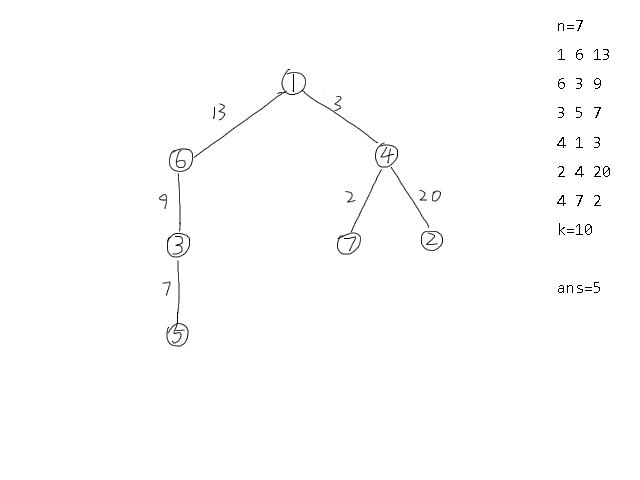
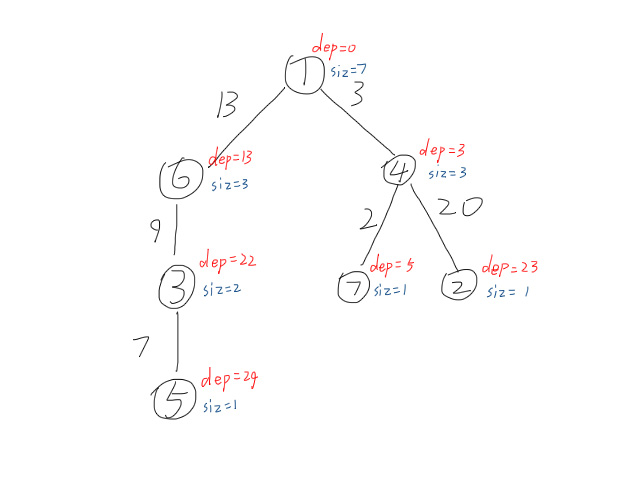
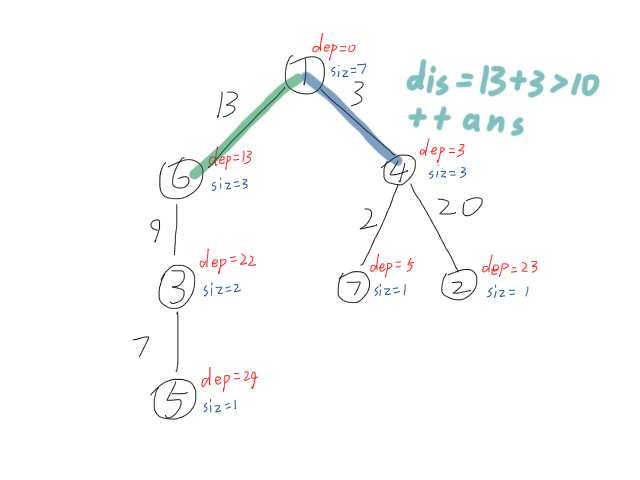
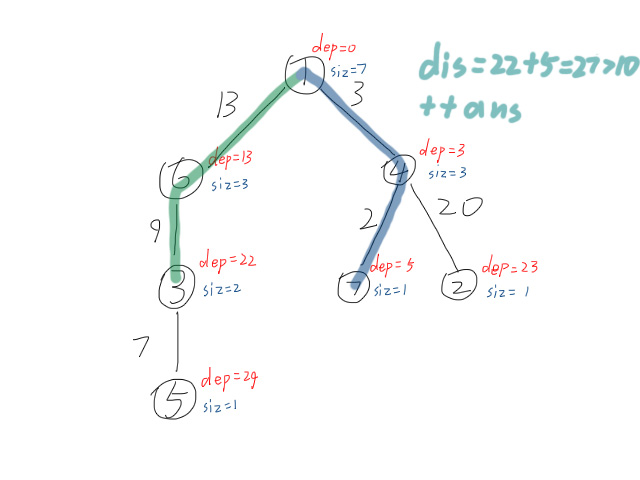
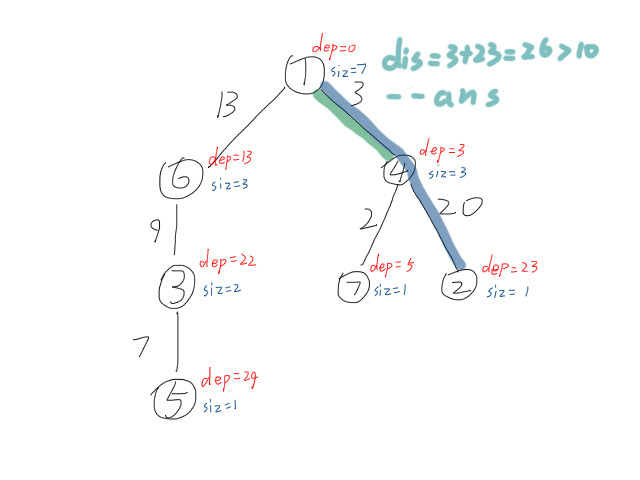
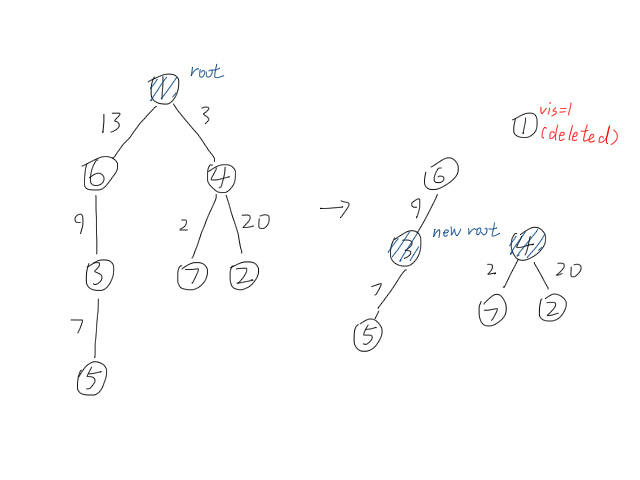
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
| #include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
char buf[1<<20], *p1, *p2;
#define getchar() (p1==p2&&(p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,1<<20,stdin),p1==p2)?0:*p1++)
inline ll read() {
ll x=0, f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while (ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if (ch=='-') f=-1; ch=getchar();}
while (ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(ch^48); ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
#define N 40010
#define v e[i].to
#define w e[i].val
int n, k, t1, t2, t3, ans;
int head[N], tot;
int siz[N], Fa[N], son[N], rt[N], cnt, h[N];
bool vis[N];
struct edge {
int to, nxt, val;
} e[N<<1];
void add_edge(int x, int y, int z) {
e[++tot].nxt=head[x], e[tot].to=y, e[tot].val=z, head[x]=tot;
}
void getroot(int u, int fa) {
siz[u]=1, Fa[u]=fa, son[u]=0;
for (int i=head[u]; i; i=e[i].nxt) {
if (v==fa||vis[v]) continue;
getroot(v, u);
siz[u]+=siz[v];
if (siz[son[u]]<siz[v]) son[u]=v;
}
if (son[u]==0) {rt[u]=u; return;}
rt[u]=rt[son[u]];
while (max(siz[son[rt[u]]], siz[u]-siz[rt[u]])>siz[u]>>1) rt[u]=Fa[rt[u]];
}
void dfs1(int u, int fa, int de) {
h[++cnt]=h[0]+de;
for (int i=head[u]; i; i=e[i].nxt) {
if (v==fa||vis[v]) continue;
dfs1(v, u, de+w);
}
}
int calc(int u, int wi) {
cnt=0, h[0]=wi;
dfs1(u, 0, 0);
sort(h+1, h+cnt+1);
int l=1, r=cnt, res=0;
while (r>=l) {
if (h[r]+h[l]<=k) res+=(r-l), ++l;
else --r;
}
return res;
}
void dfs2(int u) {
getroot(u, 0);
u=rt[u], vis[u]=1;
ans+=calc(u, 0);
for (int i=head[u]; i; i=e[i].nxt) {
if (vis[v]) continue;
ans-=calc(v, w);
dfs2(v);
}
}
signed main() {
n=read();
for (int i=1; i<n; ++i) {
t1=read(), t2=read(), t3=read();
add_edge(t1, t2, t3), add_edge(t2, t1, t3);
}
k=read();
dfs2(1);
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}
|